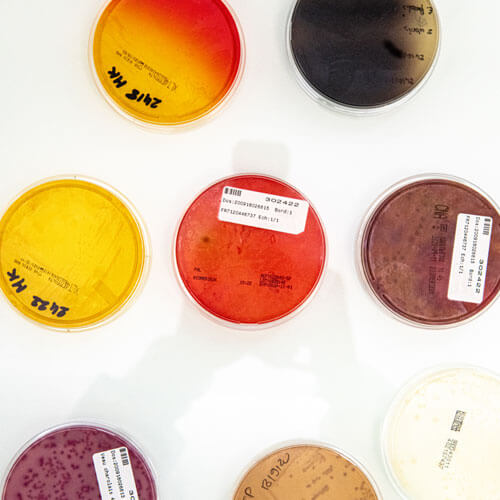
Animal health tests for poultry
As our laboratory is recognised by the French Ministry for Agriculture, we can carry out tests to screen for Salmonella and Avian Influenza Virus in poultry.
As a laboratory recognised by the French Ministry for Agriculture, we can carry out tests to screen for Salmonella and Avian Influenza Virus in poultry as part of mandatory self-checks.
Detecting antibodies or antigens from samples of animal origin.
DNA polymerase amplification (specific region of a nucleic acid) to detect it and study it.
Avian Influenza, or Fowl Plague (sometimes referred to incorrectly as Bird Flu), caused by a Type A virus, is an animal disease that can affect domesticated bird species (hens, turkeys and quail etc.) as well as ornamental or wild birds. Transmission to humans is possible.
All Avian Influenza viruses can be transmitted between birds through direct contact with the discharges of infected animals (faeces) and through contaminated water, food, equipment, clothing and shoes.
Symptoms :
Salmonella are enterobacteria that live in the digestive tracts of animals, in soil and in water. They cause Salmonellosis which represents a major problem for poultry breeders and human health.
Animals become contaminated through the intermediary of water or food dirtied by soil, but especially through the excreta of other animals, those of the same species or human beings (illegal effluent etc.).
Method : Culture
Two types of matrix :