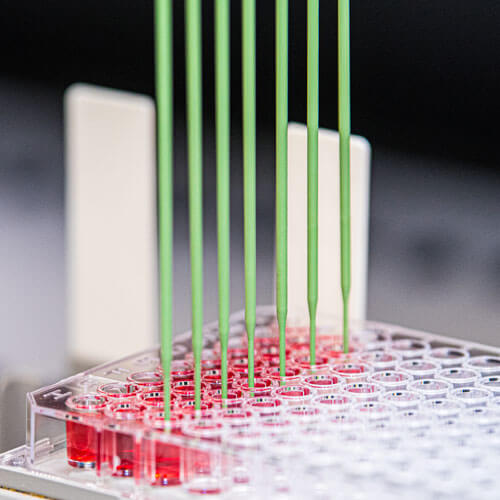
Animal health tests for swine
We can monitor epidemics in herds of pigs and develop new research methods for emerging pathologies etc.
We can monitor epidemics in herds, develop new research methods for emerging pathologies and improve knowledge, screening and the control of diseases such as Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), Porcine Respiratory Coronavirus and numerous viral or bacterial agents causing respiratory or digestive diseases.
Detecting antibodies or antigens from samples of animal origin.
DNA polymerase amplification (specific region of a nucleic acid) to detect it and study it.
Aujeszky's Disease is a viral condition caused by a herpes virus which affects domestic and wild swine and, exceptionally, carnivores and ruminants.
This disease is mainly transmitted through a direct route through close contact, salivation, nasal and conjunctival discharges and sperm.
The disease can also be transmitted indirectly through aerosols, contaminated equipment or by ingesting food products containing meat from infected pigs.
Once infected, the animal remains a carrier of the disease throughout their life and can act as a reservoir, continuing to excrete the virus.
Symptoms :Brachyspira hyodysenteriae is a bacteria present in the large intestine of several species of animal, both clinically affected and asymptomatic. It is responsible for Swine Dysentery, an infectious disease causing a type of haemorrhagic enteritis.
Swine Dysentery can spread through a herd after an infected animal is introduced. The pathogen can be spread through contaminated boots or vehicles. Rodents and birds can also carry the bacteria and contribute to its transmission.
Infection may be subclinical.
Swine Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by a bacteria, Brucella suis, transmissible to humans. The pathogen agent is transmitted through abortion and birth products from infected animals. Infection is often subclinical.
The virus is transmitted directly and indirectly by fomites containing respiratory or genital discharges from infected animals.
Among the Chlamydiaceae family, Chlamydia suis affects pigs specifically.
The main transmission route is faecal-oral. It may also be airborne.
Infection is often asymptomatic.
Classical Swine Fever (CSF), also known as Hog Cholera, is a contagious viral disease that affects domestic and wild swine.
A healthy animal can be contaminated :
Clinical signs vary depending on the virulence of the strain and the age of the animal.
Possible symptoms :Foot and Mouth is a very serious viral disease affecting livestock. Highly contagious, it is caused by an aphthovirus and can have major economic repercussions. It affects pigs and ruminants. Death rates are high among young animals.
Foot and Mouth Disease is found in all excreta and discharges of contaminated animals (it can even be present in milk and sperm). The contamination route is respiratory of oral through direct and indirect modes.
Symptoms :Type A Influenza is the virus that causes Swine Influenza Virus, also known as “Swine Flu”; a benign but contagious disease affecting the respiratory organs of pigs. The most common sub-strains are H1N1, H1N2 and H3N2.
Swine Flu can spread from one pig to another through direct or indirect contact or by minuscule droplets in the air. It can also be transmitted to humans.
Symptoms :The most well-known strain is type A, sub-type H1N1 Swine Flu, caused by a virus from the Influenza A family. It can spread from one pig to another through direct or indirect contact or by minuscule droplets in the air. It can also be transmitted to humans.
Symptoms :The disease Leptospirosis affects pig farms and can be the cause of a zoonosis. The most common serotypes are Icterohaemorrhagiae and Australis. Animals carrying the disease (reservoir hosts) pass Leptospirosis in their urine and genital discharges. The main routes of infection are digestive, respiratory or genital. The main routes of infection are digestive, respiratory or genital.
Symptoms :Method : PCR
Matrix : Serum – Urine
Method MAT (testing for antibodies using a microscopic-agglutination test, considered the benchmark method. It is used to test antibodies against serotypes of interest)
Matrix : Serum
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae is the causal agent of Enzootic Pneumonia in swine, and the co-agent of Porcine Respiratory Disease Complex (PRDC). Infection is often subclinical but where there are symptoms PRDC presents more serious clinical signs than Enzootic Pneumonia.
Symptoms :Mycoplasma spp (spp : Latin abbreviation for species in the plural form, indicating the species could not be identified with greater precision) are characterised by an absence of cell wall. It covers numerous species that are commensal or pathogenic for humans and animals.
Method : ELISAThe Parvovirus is a virus causing Swine Parvovirus (PPV), a highly contagious, infectious disease affecting pigs. Contamination occurs through the mouth or snout from infected animals or from the external environment. Venereal transmission is also possible, as is transplacental transmission.
Symptoms :Toxin-expressing strains of Pasteurella multocida causes the so-called progressive atrophic rhinitis in pigs. Progressive atrophic rhinitis is characterised by a nasal infection with atrophy nasal turbinate bones. This can often be chronic and irreversible. The most common transmission is through direct contact with infected animals.
Symptoms :Type 2 Porcine Circovirus Virus (PCV2) is a pathogen virus associated with various diseases, in particular Piglet Wasting Disease and Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome.
PCV2 spreads through direct contact. It is present in the excreta, urine and sperm of affected pigs. It may be introduced to the herd by buying an infected animal.
Possible symptoms :The death rate varies depending on the severity of the disease.
Method : ELISAPorcine Deltacoronavirus (DCVP) is an emerging disease, first spotted in 2012, caused by a virus affecting the digestive system of pigs. Clinically, the infection is similar to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus (PEDV) and Transmissible Gastroenteritis (TGE).
Transmission of the disease: through direct contact with infected pigs and indirect contact (loading/unloading bay, transport vehicles and handling and cleaning equipment). Death mainly occurs among piglets.
Possible symptoms :Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus (PEDV) is a very contagious viral swine disease caused by a coronavirus. The disease can be very severe, even fatal among piglets.
PEDV is usually transmitted through direct faecal-oral contact but can be contracted indirectly. It can be spread through clothing, boots and vehicles contaminated by the stools of infected animals.
Symptoms :Swine coronaviruses belong to the coronaviridae family and lead to respiratory or digestive problems. Animals of all ages can contract Porcine Coronavirus through direct oral contact or airborne transmission.
Possible symptoms :Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), also called “Blue Ear Disease”, is a widespread disease that has a major economic impact. It is caused by an Arterivirus. Transmission may be direct: the virus is found in faeces, semen, urine, nasal discharge and dead foetuses. Indirect transmission through vehicles is possible.
Symptoms :Salmonellosis is a disease caused by Salmonella : enterobacteria often present in animals who are healthy carriers. It is a zoonosis. Animals become contaminated through the intermediary of water or food dirtied by the excreta of other animals, or through contaminated equipment. Swine do not present clinical signs as a general rule.
Symptoms :Swine Erysipelas is a condition caused by the bacteria Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, present in numerous animal species, especially in swine which make up their main reservoir. It is a zoonosis.
The bacteria are excreted in faeces, urine and other secretions. The disease can present a variety of evolutions with different symptoms, and can survive for a long time in the external environment.
Scarpotic Mange in pigs is a skin disease caused by a parasite specific to swine: Sarcoptes scabiei var. suis. It is transmitted by close contact between sick or chronically infected animals and healthy ones.
Symptoms :Toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. It affects pigs which the parasite uses as an intermediary host. Contamination is mainly through the oral route: ingesting feed or water contaminated with sporulated oocysts. Infection in swine is usually subclinical. Sometimes the following symptoms are observed :
Symptoms :Transmissible Gastroenteritis (TGE) is a very contagious viral swine disease caused by a coronavirus. It is introduced through healthy carriers of the virus. The main transmission route is direct contact.
Symptoms :Swine Vesicular Disease is an infectious viral diseased caused by an enterovirus. On a clinical level, there is no difference between this and Foot and Mouth Disease. The infectious agent is present in ulcers, urine and excreta. The most common transmission is direct contact between animals. But indirect transmission is also frequent, whether through excreta containing the infectious agent or through the shared use of vehicles and equipment.
Symptoms :