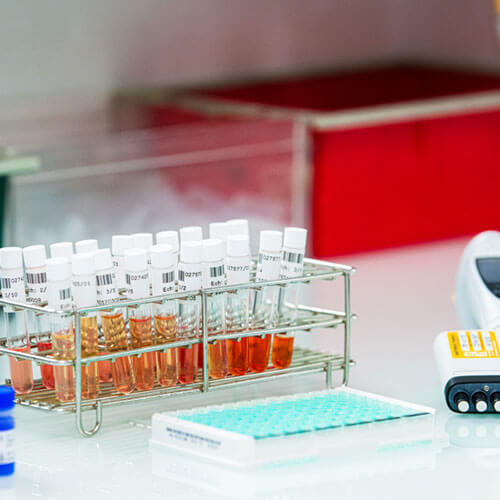
Animal health tests for ruminants : cattle / sheep / goats
We can monitor livestock epidemics, develop new research methods on emerging pathologies...
We can monitor epidemics in herds, develop new methods for detecting emerging pathologies and improve knowledge about, checking for and control of diseases such as Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR), BVD/MD, BTV and Paratuberculosis.
Detecting antibodies or antigens from samples of animal origin.
Amplification of DNA polymerase (of a specific region of a nucleic acid) for detection and analysis.
Babesiosis or Bovine babesiosis is a serious parasitic disease affecting adult cattle, transmitted mainly by ticks.
Bovine babesiosis is due to a protozoan of the genus Babesia, a microscopic parasite that lives in the red blood cells of infected animals. The main species involved are Babesia bovis, B. bigemina and B. divergens. The main source of contamination is a bovine carrier, often asymptomatic.
Symptoms :Theileriosis is a tick-borne parasitic disease caused by a protozoan (Theileria spp.) that affects red blood cells in cattle.
Symptoms :Bovine herpes virus 4 (BoHV-4) causes a reproductive disease in cattle. The virus is transmitted directly and indirectly, e.g. by fomites containing respiratory or genital discharges from infected animals.
Symptoms :Two methods :
Bluetongue virus (BTV), is a viral disease caused by an Orbivirus. It is transmitted by a vector, a midge of the Culicoides genus. It mainly affects sheep and cattle.
Symptoms :Methods :
Besnoitiosis or “Elephant Skin Disease” is a non-contagious, parasitic bovine disease that is rising sharply in France due to the introduction of infected cattle. Contamination occurs when cattle are stung by insects such as horseflies and stomoxes or the re-use of a contaminated needle for group injections.
Besnoitiosis is caused by a microscopic protozoan parasite: Besnoitia besnoiti. It affects all cattle, especially calves from one year old and males who can become permanently sterile.
Bovine coronavirus belongs to the large family of Coronaviridae and is implicated in two major clinical syndromes: respiratory infections and neonatal enteritis.
Transmission is faecal-oral and respiratory, with an incubation period of about 24 hours.
Symptoms :Methods :
Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD), is an infectious disease caused by a pestivirus.
We can distinguish between two modes of transmission of the virus: horizontal transmission (through close and direct contact between an animal excreting the virus and a healthy animal); vertical transmission: a gestating cow can transmit the virus to its foetus via the placental barrier (the foetus dies or develops into a PI animal : Persistent Infection).
Symptoms :Methods :
The infection caused by Brucella ovis is the contagious Epididymitis associated with reduced fertility in sheep.
Symptoms :Methods :
Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by a bacteria of the Brucella genus, common to numerous species of animal. Brucellosis usually spreads during birthing or aborting. It is a zoonosis.
Symptoms :Methods :
Spirochetes found in the digestive tract cause campylobacteriosis, a sexually transmitted disease. Contamination is mainly caused by natural breeding.
Symptoms :Methods :
Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus (CAEV), is a viral disease specific to goats. Contamination occurs through the ingestion of infected colostrum and milk, through the respiratory tract or blood (contact with an infected animal or blood). Adults infect each other during milking through contaminated liners.
Symptoms :Methods :
In ruminants (especially sheep), reproductive problems are believed to be mainly attributable to the Chlamydia abortus species. But two other species, Chlamydia pecorum and Chlamydia psittaci, may also occasionally be involved.
Sources of infection are mainly feces, but also the aborted products and milk from infected females. Contamination mainly occurs via the digestive and respiratory tracts.
Symptoms :Methods :
Parasitic infestation of ruminants by common fluke (Fasciola hepatica) is called Fasciolosis. The development cycle includes a freshwater snail (the intermediate host).
Consequently, animals can become infested with fluke in fields with wet zones. The animal becomes contaminated by ingesting immature forms (metacercariae) of Fasciola hepatica, which then accumulate in the bile ducts.
Symptoms :Methods :
Cryptosporidiosis is a serious intestinal disease affecting ruminants, transmissible to man, caused by a protozoan parasite: Cryptosporidium parvum. It mainly affects new-borns, aged under two weeks old. The disease is highly contagious and is transmitted by oocysts via the faecal-oral tract. These destroy intestinal cells. Water as well as boots and clothes can also be vectors for oocysts. Can cause death.
Symptoms :Methods :
E.coli is part of the normal intestinal flora of mammals. In calves, the normal amount is around106 bacteria/g of faeces. The main disease caused by pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli is Neonatal Calf Diarrhoea. Testing can be carried out for various adhesion factors playing a pathogenic role: F5, CS31A, F17 and FH1 etc. The mode of transmission is faecal-oral. Death may occur.
Symptoms :Methods :
Enzootic bovine leukosis (EBL) is disease of cattle. It is caused by a virus from the Retroviridae family. It is mainly an infected animal’s blood that is contagious, followed by its milk and its colostrum. Natural transmission depends on the transfer of infected cells, for example during parturition, or through the intermediary of stinging arthropods (ticks and mosquitoes etc.). Artificial transmission occurs, e.g. by blood-contaminated needles, surgical equipment, gloves used for rectal examinations, or through the non-heat-treated colostrum.
Most infected cattle will display no clinical signs. If there are symptoms :
Symptoms :Methods :
Gangrenous Coryza, or Malignant Catarrhal Fever, is a sporadic general disease in cattle, caused by a gamma herpes virus, Ovine Herpes Virus 2 (OHV2). Sheep are healthy carriers and constitute a reservoir for the virus. The mode of transmission is the oropharyngeal or digestive tract. The mortality rate is very high.
Symptoms :Methods :
Histophilus somni is a bacteria from the Pasteurellaceae family which can cause a respiratory disease in cattle. It can be associated with other bacterial agents to cause Enzootic Pneumonia (EP). Transmission occurs via direct and indirect contamination, through discharge and infected mucus.
Symptoms :Methods :
Bovine Hypodermosis, also known as Cattle Grub or Warble Fly Infestation is a parasitic disease by Hypoderma bovis and H. lineatum flies laying eggs. After hatching, they penetrate into the skin and migrate to the conjunctive tissue and the larvae remain in the sub-cutaneous dorsal tissue.
Symptoms :Methods :
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR), is a highly contagious viral disease caused by a bovine herpes virus: BHV1. Like all herpes viruses, after an initial infection BHV1 can survive in a dormant state in the infected animal and re-emerge at any time.
The BHV-1 virus is mainly transmitted through direct contact.
There are two contamination routes :
– “Nose to nose” contact: main route.
– Servicing.
Vectoral transmission (bucket, ropes and nose-rings etc.) is possible.
Symptoms :Methods :
Influenza D is a virus that can be implicated in bovine respiratory pathologies and flu-like symptoms.
Symptoms :Methods :
Leptospirosa is a bacteria that causes Leptospirosis, a zoonosis disease. It has a worldwide distribution and affects many animal species. Carrier animals (reservoir hosts) are rodents who pass leptospires in their urine, thus contaminating pasture, drinking water and food. Leptospires can be passed in the urine of infected cattle for a very long time and can survive outside the host animal if the environment is warm and humid. Semen also constitutes another source of infection. As a result, an infected bull can carry the bacteria and infect females during mating.
Symptoms :Methods :
Listeria, specifically Listeria monocytogenes, is the bacteria that causes Listeriosis.
Listeria is a bacteria found in soil and in water. Ruminants mainly become contaminated through grass, incorrectly-stored fodder or water.
Methods :
Visna – Maedi is a viral disease in sheep caused by an oncornavirus which appears is animals aged over two years. Animals are contaminated very young through the colostrum, milk and respiratory discharges of infected sheep. Vertical transmission from a sheep to a lamb is possible.
Symptoms :Methods :
Mannheimia haemolytica is the principal bacterium isolated from respiratory disease in feedlot cattle and is a significant component of enzootic pneumonia in neonatal calves, sheep and goats. It affects the lungs.
The multiplication and diffusion capacity of this bacteria is very high in poor environmental conditions. Hence the often high contagiousness of this disease through direct contact between animals and environmental contamination.
Symptoms :Methods :
A bacteria specifically affecting small ruminants (sheep and goats) causing Contagious Agalactia. M. agalactiae was initially considered the only agent causing this disease. M. mycoides mycoides and M. capricolum capricolum may also be involved. Transmission may be direct (respiratory) or indirect (milking)/ Vertical mother/new-born transmission is also possible.
Symptoms :Methods :
A bacteria specifically affecting cattle, causing Mycoplasmosis, a contagious, infectious disease. M.bovis may be associated with other viral and/or bacterial pathogen agents.
Transmission is by direct contact with an infected animal, often a healthy carrier, or from mother to calf. The disease usually evolves in an isolated way. In some cases, the presence of certain conditions can lead to widespread contamination.
Symptoms :In adults :
In young (EIPB) :
Methods :
Mycoplasma wenyonii infects red blood cells in cattle. This infectious agent is transmitted by stinging insects. After an incubation period of 1-3 weeks and a clinical illness of 8-10 days the animal remains a carrier.
Symptoms :Methods :
Mycoplasms are bacteria that trigger a disease in numerous species of animal. In cattle, we mainly see Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia and Mycoplasma bovis diseases.
Methods :
Neospora caninum is a single-celled parasite from the coccidian family. It was first discovered in dogs, its definitive hosts, and then in cattle, intermediary hosts, where it seems to be responsible for some 10-15% of abortions.
There are two types of transmission :
Methods :
Gastrointestinal strongyles are round parasitic worms in the digestive tract present in all cattle who become infected while grazing. Gastrointestinal strongyles are extremely common and Osetertagia ostertagi is the most pathogenic of them all.
There are two possible forms :
- Type I Ostertagiosis: a parasitic gastritis in calves in their first grazing season.
- Type II Ostertagiosis: due to the encysted larvae emerging from the wall of the abomasum. This is a severe form.
Symptoms (Type II) :Methods :
Paratuberculosis is an enteritis affecting ruminants. The pathogen agent is a mycobacteria called Mycobacterium paratuberculosis.
Contamination usually takes place in the first few weeks or months of life. The faeces of infected adult animals represents the main source of contamination. Calves may also be contaminated either towards the end of gestation via the transplacental route or through the colostrum.
Symptoms (in adult animals) :Two Methods :
This bacteria is often present in the respiratory mucous membranes of mammals and can cause bronchopneumonia, particularly in ruminants.
Symptoms (general and/or respiratory) :In several species, a type of septicaemic or suppurating sores may occur.
Methods :
The Type III Parainfluenza virus is responsible for flu syndromes in cattle.
Symptoms :Bacterial complications are common.
Methods :
Q Fever is a zoonotic disease caused by Coxiella burnetii, a small bacteria, highly resistant to the environment, affecting ruminants. The main mode of transmission is the inhalation of infected aerosols from abortion products and faeces ; the bacteria is spread by the wind, dust, ticks, insects, wild or domestic animals, rodents and birds. Infection is often asymptomatic but can express itself through various clinical signs.
Symptoms :Methods :
Respiratory Syncytial Virus is the main agent responsible for flu symptoms in cattle.
Symptoms :Bacterial complications are common.
Methods :
Salmonella are enterobacteriaceae present in soil and water. They can colonise the digestive tract of a great many animal species. They cause Salmonellosis.
Animals become contaminated through the intermediary of water or food dirtied by soil, but especially through the excreta of other animals. Poultry or rodents can be sources of contamination on ruminant livestock farms.
Symptoms :Methods :
Salmonella abortus ovis is an enterobacteriaceae specific to sheep.
Animals are contaminated through abortion and birthing products which make up a virulent primary material.
Symptoms :Methods :
Schmallenberg Virus, or SBV, causes an infection affecting ruminants (cattle, sheep and goats). Essentially vectoral, this arbovirus is transmitted by haematophagous insects from the Culicoides family (as with BTV).
Symptoms :Methods :
Toxoplasmosis is a disease of parasitic origin mainly affecting small ruminants and, more rarely, cattle. The agent is an intracellular parasite, Toxoplasma gondii.
Ruminants are contaminated via the oral route: ingestion of food or water contaminated with excreta from infected pregnant cats containing sporulated oocysts. Transmission via the transplacental route is also possible.
The disease is often subclinical in adults.
Symptoms :Methods :